Low End Tidal Co2 Range
All had hemodynamic measurements to confirm the diagnosis of pph. Co2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism, which gets transported in the blood to the lungs for elimination.


Understanding end tidal co 2 monitoring.
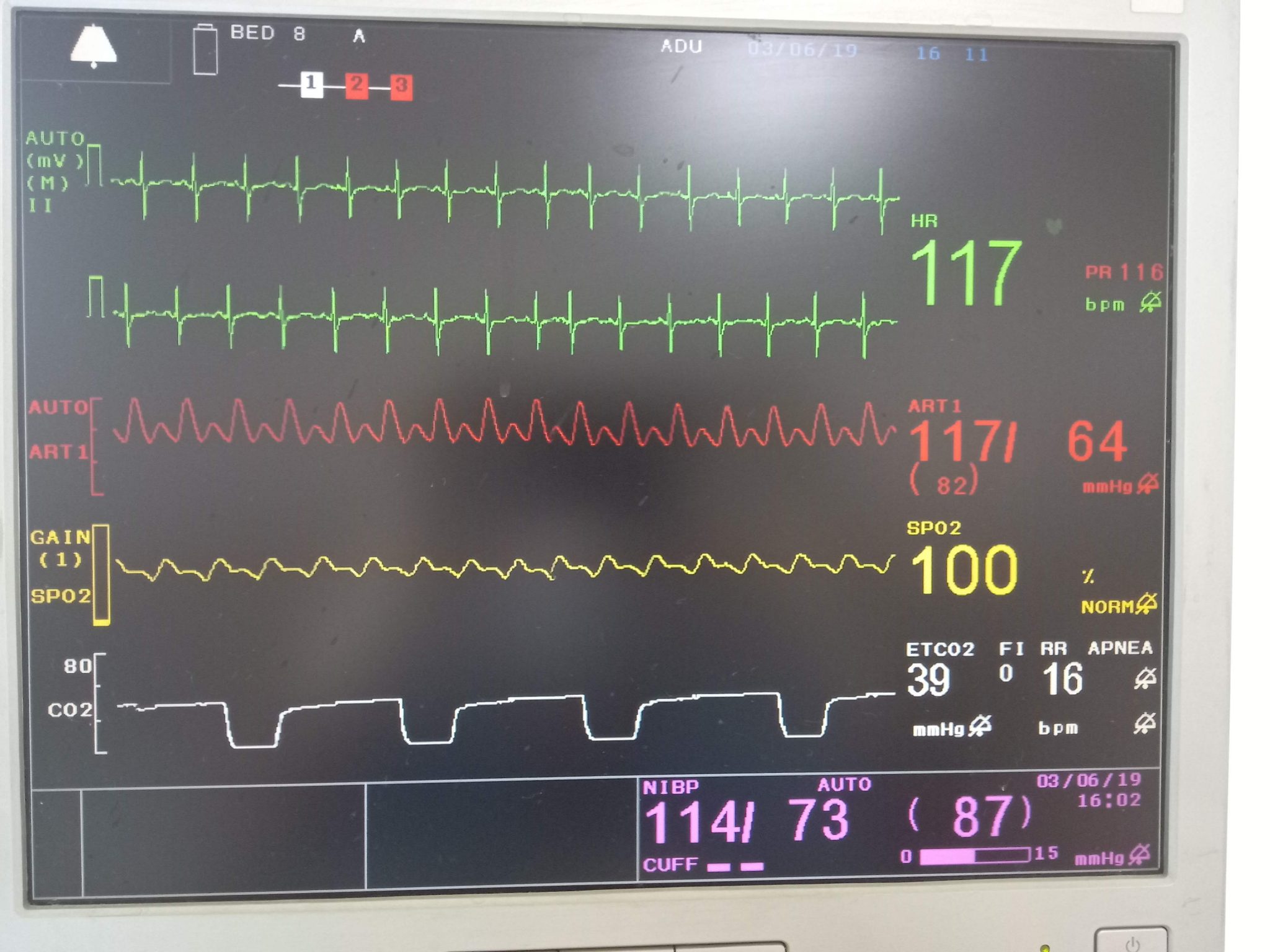


Low end tidal co2 range. 78% nitrogen 21% oxygen 1% co2 and other gases exhaled gases: Most medical sources define hypocapnia as less than 35 mm hg for partial co2 pressure in the arterial blood. Normal etco2 is 35 to 45 mm hg.
Normal minute ventilation (about 200 ml/kg/min for dogs and cats) in conscious animals with normal lungs results in an arterial and therefore alveolar co 2 partial pressure of 35 to 45 mm hg. The rate of co2 production in all groups of people is the same. •beginning of plateau is low •end of plateau shows a peak (ppv pushes co 2 to monitor) •may see similar pattern in obesity or pregnancy return of spontaneous ventilation during cpr:
But even in an ideal physiologic state, a difference of 2 to 5 mm hg usually exists. We performed cardiopulmonary exercise testing (cpet) in 52 pph patients. Etco 2 ≤30 mmhg may be associated.
The amount of co2 at the end of exhalation, or. But even in an ideal physiologic state, a difference of 2 to 5 mm hg usually exists. Mmhg relate to the air we breath:
The arterial co2 value for normal breathing at rest is 40 mm hg (or about 5.3% co2 partial pressure at sea level). The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much co 2 is present at each. Another term “alveolar hypocapnia” describes low co2 levels in.
Phase iv is when inhalation begins, and the level of co2 begins to drop rapidly. It is best to get an abg along side the end tidal to calculate the patients shunt. Similarly, you may ask, what does etco2 mean?
Capnography waveforms, etco2, and breathing patterns. Capnography in low perfusion case scenario 45 35 0 25 low etco 2 seen in ventilation controlled low cardiac output. End tidal co 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.
Repiratory rate and depth (tidal volume) which determine minute ventilation and therefore arterial co2. Measuring end tidal co2 dalton’s law: Capnography can measure ventilation by.
Hence, co 2 levels in the expired gas is a parameter that accurately reflects minute ventilation. New england journal of medicine 337 (5): Normal difference between paco 2 and etco 2.
Also know, what are normal etco2 levels? We know that elevated etco2 (hypercapnia) occurs during hypoventilation, and a decrease in etco2 (hypocapnia) occurs with hyperventilation. As stated before end tidal is slightly different.
•ensure proper rate (approximately 100/min) •ensure proper depth with adequate release/recoil of thorax (1/2. The plateau observed at the end of the In conditions of normal breathing (6 l/min, 12 breaths/min, 500 ml for tidal volume) etco 2 is very close to alveolar co2.
Once that has been done you can use an end tidal co2 monitor as opposed to drawing multiple abg's. •measurement of a low etco 2 value (< 10 mmhg) during cpr in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement.









0 Response to "Low End Tidal Co2 Range"
Posting Komentar